Lanka IOC PLC, a leading player in Sri Lanka’s petroleum industry, has faced a tumultuous fiscal year ending March 31, 2024. This report delves into the financial performance, key ratios, and profitability of the company, highlighting significant trends and providing a comprehensive analysis of its financial health.
Financial Performance Overview
Revenue and Profitability
Lanka IOC PLC’s financial performance for the year ending March 31, 2024, has seen substantial fluctuations:
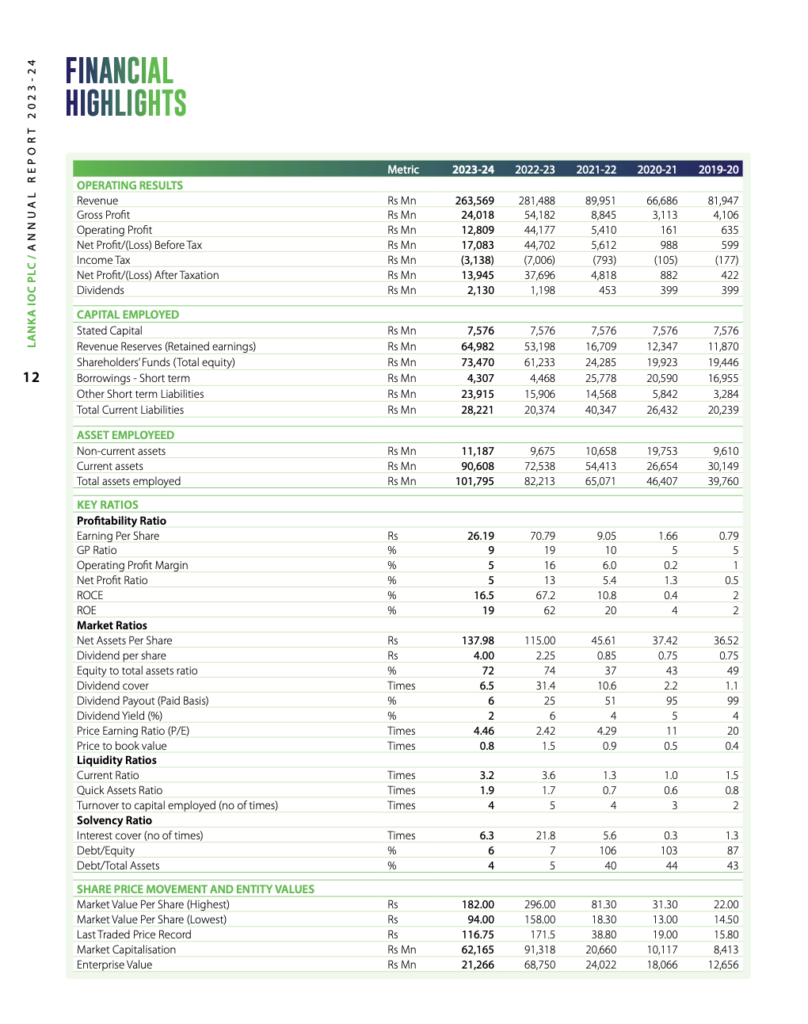
- Revenue: The company reported a total revenue of Rs 263,569 million, down from Rs 281,488 million in the previous year. This 6.4% decrease reflects challenges in maintaining market share and achieving sales targets amid a volatile economic environment.
- Gross Profit: The gross profit for the year was Rs 24,018 million, a sharp decline from Rs 54,182 million in 2022-2023. This indicates increased cost pressures and difficulties in managing the cost of goods sold effectively.
- Operating Profit: The operating profit stood at Rs 12,809 million, significantly lower than the Rs 44,177 million recorded in the prior year. The decrease underscores inefficiencies in operational management and higher operational costs.
- Net Profit Before Tax: Net profit before tax dropped to Rs 17,083 million from Rs 44,702 million, reflecting the overall downturn in profitability.
- Net Profit After Tax: Similarly, net profit after tax declined to Rs 13,945 million, compared to Rs 37,696 million in the previous fiscal year.
Key Financial Ratios
Profitability Ratios
The profitability ratios highlight the company’s ability to generate earnings relative to revenue, operating costs, and equity:
- Gross Profit Ratio: The gross profit ratio decreased to 9% from 19%, indicating a reduction in the company’s margin due to increased costs.
- Operating Profit Margin: This margin fell to 5% from 16%, showing significant challenges in managing operating expenses.
- Net Profit Ratio: The net profit ratio also declined to 5% from 13%, reflecting the overall reduction in net profitability.
Return Ratios
The return ratios provide insights into the efficiency of the company in generating returns for shareholders:
- Return on Capital Employed (ROCE): The ROCE dropped sharply to 16.5% from 67.2%, indicating lower returns on the capital employed in the business.
- Return on Equity (ROE): The ROE decreased to 19% from 62%, showing reduced profitability relative to shareholders’ equity.
Liquidity Ratios
The liquidity ratios assess the company’s ability to meet its short-term obligations:
- Current Ratio: The current ratio slightly decreased to 3.2 from 3.6, indicating a modest reduction in the company’s liquidity position.
- Quick Ratio: The quick ratio improved to 1.9 from 1.7, reflecting better short-term liquidity excluding inventories.
Solvency Ratios
The solvency ratios illustrate the company’s capacity to meet long-term obligations:
- Debt to Equity Ratio: The debt to equity ratio decreased slightly to 6% from 7%, indicating a marginal reduction in leverage.
- Interest Coverage Ratio: The interest coverage ratio fell to 6.3 times from 21.8 times, showing a decreased ability to cover interest expenses with operating profit.
Market Ratios
Market ratios provide insights into the company’s valuation in the stock market:
- Earnings Per Share (EPS): EPS dropped to Rs 26.19 from Rs 70.79, reflecting the overall decline in net profitability.
- Dividend Per Share: The dividend per share increased to Rs 4.00 from Rs 2.25, indicating a higher payout to shareholders despite lower earnings.
Conclusion
The fiscal year ending March 31, 2024, has been challenging for Lanka IOC PLC, with notable declines in revenue, profitability, and key financial ratios. The company must address its operational inefficiencies, manage costs more effectively, and explore new revenue streams to improve its financial health and return to sustainable growth.